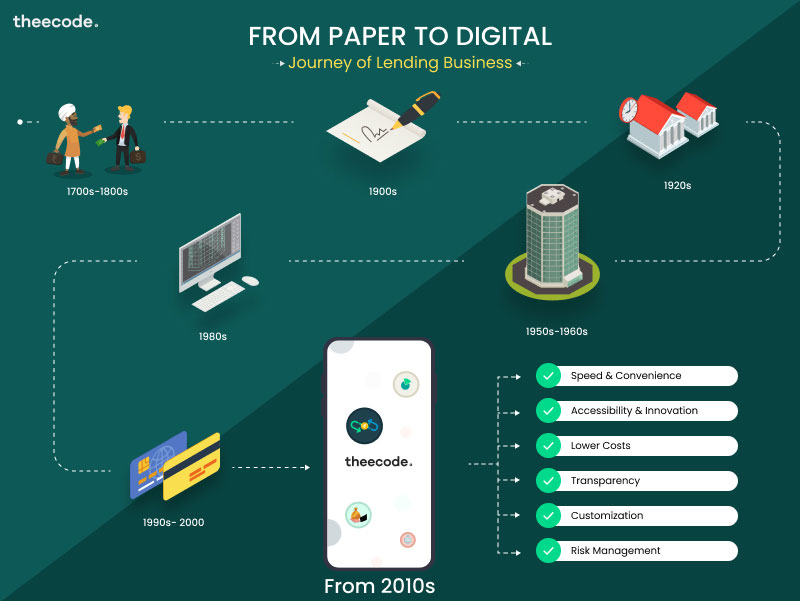
From Paper to Digital - Journey of Lending Business
The lending business has come a long way from paper-based processes to digital
lending platforms. In the past, getting a loan was a cumbersome and
time-consuming process. The borrower had to visit the lender's office multiple
times, submit a pile of documents, and wait for days or even weeks for the loan
to be approved. However, with the advent of digital technology, the lending
process has become much simpler and faster.
The timeline of the loan process across the decades
-
1700s-1800s: The earliest recorded loans were provided by
pawnbrokers and moneylenders who would lend money against collateral.
These loans were typically small and short-term and were provided to
individuals who were unable to access traditional banking services.
-
1900s: The modern lending industry began to take shape with the
emergence of consumer finance companies, such as Household Finance
Corporation and Beneficial Finance Company. These companies provided
loans to consumers who did not have access to bank loans or credit
cards.
-
1920s: The first credit bureaus were established to track
consumer creditworthiness. The most famous of these was Equifax, which
was founded in 1899 as a credit reporting agency for the mercantile
industry.
-
1950s-1960s: Banks began to play a larger role in the lending
industry, offering loans to consumers and businesses. This was made
possible by the introduction of credit scoring, which allowed banks to
assess the creditworthiness of borrowers more accurately.
-
1980s: The securitization of loans began to gain popularity, as
lenders packaged loans together and sold them to investors. This allowed
lenders to generate more liquidity and reduce risk.
-
1990s: The internet began to emerge as a viable platform for
conducting business, and online lenders such as E-Loan and LendingTree
began to emerge.
-
2000s: The financial crisis of 2008 had a significant impact on
the lending industry, as lenders tightened their lending standards and
many traditional lenders went out of business. This created an
opportunity for digital lending platforms to emerge, such as LendingClub
and Prosper, which leveraged technology to connect borrowers with
investors.
-
2010s-present: The digital lending industry continued to grow
and evolve, with the introduction of new products and services such
as peer-to-peer lending, crowdfunding, and mobile lending apps. The
rise of blockchain technology has also opened up new possibilities
for the lending industry, with the emergence of decentralized
lending platforms such as SALT and ETHLend.
With the rise of digital lending platforms, the loaning process has
become even more streamlined and efficient. Borrowers can apply for
a loan online, provide their documentation electronically, and
receive a loan decision within minutes. The use of big data and
machine learning algorithms has also enabled lenders to make more
informed lending decisions and reduce the risk of default.
As technology progressed, lenders started adopting computerized
systems to manage their lending processes. This involved digitising
the application process and using software to automate various
aspects of the loan underwriting process. However, these systems
were still largely reliant on paper-based documentation, and
borrowers still had to physically submit their documents to the
lender's office.
The real revolution in lending came with the advent of digital
lending platforms. These platforms are essentially online
marketplaces that connect borrowers with lenders. Borrowers can
apply for a loan online, upload their documents electronically, and
receive a loan decision within minutes. Lenders, on the other hand,
can access a large pool of potential borrowers and use advanced
algorithms to underwrite loans quickly and accurately.
Key benefits of the switch from paper to digital lending platforms:
- Speed and Convenience:
Digital lending processes are typically much faster and more convenient
than traditional lending processes. Borrowers can apply for loans online
from anywhere, at any time, and receive a loan decision within minutes
or hours, rather than days or weeks.
-
Accessibility: Digital lending platforms have made it easier for
underserved borrowers, such as those with thin credit files or low
credit scores, to access credit. By using alternative data and machine
learning algorithms, digital lenders are able to make more informed
lending decisions and provide loans to borrowers who may not have been
able to get approved by traditional lenders.
-
Lower Costs: Digital lending platforms are often able to offer
lower interest rates and fees than traditional lenders, due to their
lower overhead costs and more efficient loan processing.
-
Transparency: Digital lending platforms typically offer more
transparency into the lending process, providing borrowers with clear
information about interest rates, fees, and loan terms.
-
Customization: Digital lending platforms are often able to offer
more customized loan products that are tailored to individual borrowers'
needs. By leveraging big data and machine learning, lenders can better
understand borrowers' financial situations and offer loan products that
are better suited to their needs.
-
Risk Management: Digital lending platforms are often able to
better manage risk by using advanced analytics and machine learning
algorithms to assess borrowers' creditworthiness and identify potential
defaults before they occur.
-
Innovation: Digital lending platforms are often at the
forefront of innovation in the lending industry, using new
technologies such as blockchain and artificial intelligence to
develop new products and services that are more efficient, secure,
and user-friendly
However, there are also some challenges associated with digital
lending. One of the main challenges is the need to ensure data
privacy and security. Digital lending platforms collect and store a
large amount of personal and financial information, and there is a
risk of this information being compromised. Lenders need to invest
in robust security measures to protect their borrowers' data
Another challenge is the need to ensure fair lending practices.
Digital lending platforms use algorithms to underwrite loans, which
can sometimes result in unintended biases. For example, if the
algorithm is trained on historical data that reflects existing
preferences in the lending system, it may perpetuate those biases.
Lenders need to be vigilant and ensure that their algorithms are
fair and unbiased.
Coping up with the modernisation of lending while making sure ist
highly secure, safe and efficient can be a tough battle to be in. It
makes it equivalently important to choose the right technology to
streamline your entire lending process. Theecode technologies are a
reliable and efficient platform for digital lending, especially when
it comes to addressing the challenges associated with data privacy,
security, and fair lending practices. With its focus on implementing
robust security measures to protect borrowers' sensitive information
and ongoing efforts to monitor and adjust algorithms to avoid
unintended biases, Theecode technologies take proactive steps to
tackle the challenges of digital lending.
However, it is worth noting that the digital lending industry is
constantly evolving, and new challenges may emerge over time.
Therefore, Theecode remains vigilant and stays up-to-date with the
latest developments in the industry to ensure that we are providing
a safe and fair lending experience to our customers.
Fast, Efficient, and Secure lending with Theecode